If you’re responsible for regulatory compliance, you might be curious about the relationship between AI and risk management.
As in many other business functions, AI presents a wide range of benefits in risk management, ranging from greater accuracy to enhanced threat detection.
However, with third-party services handling valuable data, the technology also presents some risks.
In this article, you’ll learn about the benefits and applications of AI in risk management. You’ll also discover the potential risks involved and best practices for using risk management AI effectively.
What’s the role of AI in risk management?
The role of AI in risk management is to identify, assess and mitigate risk with speed and accuracy.
AI risk management software uses artificial intelligence to analyze vast amounts of data – including transactional, behavioral, historical and real-time data.
AI risk management uses machine learning to detect patterns that traditional methods might miss. The tools also predict outcomes and automate responses to different types of risk. These include:
Market or investment risks
Security or cybersecurity risks
Compliance or regulatory risks
Fraud or credit risks
Risks relating to the geopolitical landscape (e.g., climate change)
A wide range of sectors use the technology. These include financial services, healthcare and business operations.
Here are some of the most common use cases for AI risk management software in business:
Compliance monitoring | The technology helps with regulatory compliance management by scanning policies and activities for breaches. |
Corporate governance | AI evaluates management practices and monitors internal controls to identify ethical risks. |
Cybersecurity threat detection | AI can protect companies from cyberattacks by monitoring systems for suspicious activity. |
Supply chain risk management | AI can forecast supply chain disruptions by analyzing external factors and supplier data. |
Operational risk management | AI detects operational inefficiencies and identifies system failures that could cause business disruption. |
Fraud detection | AI risk management tools analyze transaction patterns and anomalies to detect fraudulent activities. |
Credit risk assessment | In financial institutions, AI analyzes a customer’s financial data and credit history to assess the probability of repayment issues. |
With so many use cases, AI risk management software offers businesses several benefits.
What are the benefits of using an AI risk management tool?
Here are some of the biggest benefits of using AI to support risk management:
Supporting regulatory compliance
AI risk management applications help organizations remain compliant with relevant rules and regulations by:
Processing large amounts of data to detect patterns and anomalies that may signal compliance breaches
Automating compliance checks and reporting to ensure accuracy
Streamlined auditing with structured records of risk assessments and decision-making processes
Minimizing risk through enhanced threat detection
AI-powered risk management tools improve threat detection by:
Continuously monitoring transactions, operations and external threats in real time
Using machine learning algorithms to identify emerging risks
Providing automated threat alerts and recommended actions to facilitate a fast response
Improving decision-making
AI risk management software helps business owners and leaders make better-informed decisions by:
Offering predictive insights through the analysis of historical and real-time data
Identifying potential risks and opportunities with greater accuracy than other methods
Producing data-driven outputs to support strategic management and the strategic planning process
Download Your Sales and Marketing Strategy Guide
Mitigating future risk
The software can help businesses reduce their exposure to future risk by:
Predicting the impact of various scenarios through advanced simulations
Using learning algorithms to adapt to new threats and regulatory changes
Highlighting opportunities to improve their systems, processes and procedures for managing and mitigating risk
AI-powered risk management software helps businesses streamline processes and mitigate risks more effectively. This allows them to strengthen their business operations, improve decision-making and increase resilience to future challenges.
What are the potential risks of using AI in risk management?
As with the use of AI in any business function, there are some dangers involved in adopting the technology for risk management. Let’s take a look at some of the potential pitfalls. We’ll then share best practices to help you eliminate the risks:
AI can make mistakes
AI relies on the accuracy of its algorithms and training data to produce its outputs. Although it might seem to, it doesn’t understand the tasks it’s performing. It’s therefore prone to making mistakes.
This lack of understanding is a well-known drawback of using AI to make business decisions. In Pipedrive’s State of AI in Business report, a “lack of trust in AI outputs” was one of the most common barriers to adoption.
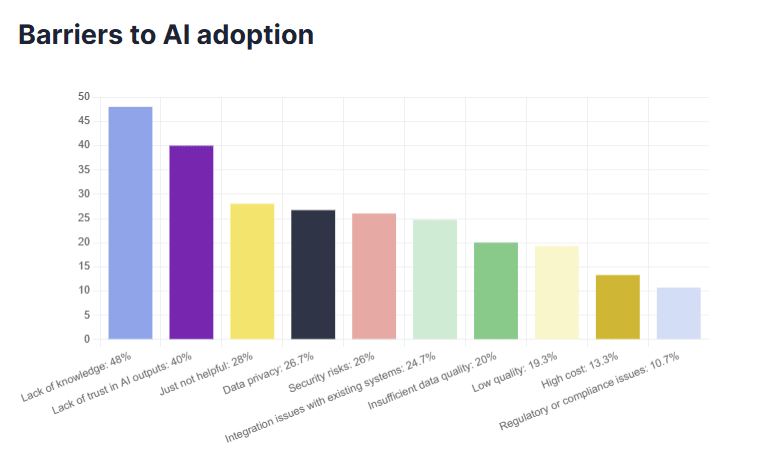
In risk management, an AI system could identify a risk incorrectly or fail to highlight an existing threat. These mistakes can all harm business decision-making processes.
For example, an AI system might generate a “false positive” and incorrectly highlight a prospect as a fraud risk. As a result, the business could miss out on acquiring a new customer.
If AI fails to identify the threat of a cyber attack and customer data is compromised, the error would result in significant reputational damage.
AI can mishandle customer data
AI risk management tools analyze large volumes of sensitive customer data. Without proper governance, these systems can be vulnerable to data breaches and misuse.
For example, some AI-powered fraud detection tools may retain customer data longer than necessary. Other systems may not comply with relevant data protection legislation, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for data about European residents and citizens.
AI can generate biased outputs
If an AI system trains on biased data, it can generate outputs reinforcing that bias.
For example, an AI-powered customer segmentation model might train on data that over-represents customers from a certain demographic.
In risk assessment, AI models can reinforce existing bias when performing tasks like financial risk scoring and fraud detection. For example, they can predict a disproportionate threat level from customers based in certain regions.
AI can create a compliance risk by using third-party data
Many AI models rely on third-party data, which might not be accurate or compliant with data protection laws. For example, an AI tool that scrapes online data to obtain customers’ credit scores might violate consumer protection laws.
Running into any of these pitfalls can have serious repercussions for businesses, ranging from reputational risks to financial penalties and even criminal prosecution.
Catch more hot leads before they bounce
7 best practices for using risk management AI effectively
While there are some risks involved in using AI for risk management, there are steps you can take to address them. Here are seven best practices to ensure you use AI responsibly and transparently:
1. Train tools on high-quality data
The AI algorithms in risk management tools rely on high-quality and diverse data to deliver valuable outputs and genuine risk mitigation. For those using the software, this means:
Providing well-structured datasets that are complete and representative of the entire relevant population (i.e., not weighted in favor of a particular customer demographic or socioeconomic group)
Incorporating unstructured data sources (e.g., emails, reports, policy documents) for the tool to process using natural language processing (NLP), an application of generative AI techniques
Providing accurate and timely data throughout the AI lifecycle to ensure the model remains up-to-date and effective at all times
2. Maintain human oversight
In business, AI should enhance human judgment – not replace it. This is especially true in risk management, where the stakes are so high. Keep humans in the loop by:
Benchmarking AI-driven risk assessments against historical data to evaluate the outputs for accuracy and consistency
Ensuring risk professionals review AI-generated outputs, particularly in unusual scenarios where learning algorithms may produce unexpected results
Conducting regular audits to assess the ongoing effectiveness and accuracy of AI systems
3. Comply with relevant AI legislation
With AI technology becoming more widespread, it’s good practice to watch the latest tech news and stay updated with evolving legislative discussions.
For instance, while there’s currently no federal legislation for AI use in the US, it’s good practice for businesses to follow the guidelines outlined in the NIST AI Risk Management Framework. Companies marketing to the EU must comply with the EU AI Act. (We discuss these guidelines and requirements in-depth below.)
Catch more hot leads before they bounce
4. Implement bias detection and fairness checks
If an AI system trains on biased data, it can generate unfair or discriminatory outputs. It’s important to mitigate this risk by:
Using bias-detection tools to identify potential biases in AI algorithms
Conduct regular assessments to ensure AI-driven decisions don’t disproportionately affect specific groups
Use benchmarking techniques to compare AI-generated outputs against diverse data sources and alternative models
5. Implement robust cybersecurity measures
AI systems are particularly susceptible to cyber-attacks because they rely on vast amounts of data and complex algorithms. These are vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
Put strong cybersecurity measures in place for AI for risk management by:
Safeguarding AI models and data with encryption, access controls and continuous monitoring
Establishing clear incident response protocols for security breaches
Alerting relevant stakeholders to breaches promptly and taking corrective action in line with company policy
6. Follow best practices for recording risk management activities
Accurate documentation is an important part of the AI risk management process, as it helps ensure accountability and compliance.
This means maintaining detailed audit trails of AI-driven risk decisions. It’s also important to accurately record the completed risk management processes for customers in your customer relationship management (CRM) software.
Pipedrive includes functionality for recording completed compliance checks – e.g., Know Your Customer (KYC) verification checks – as shown in the image below.
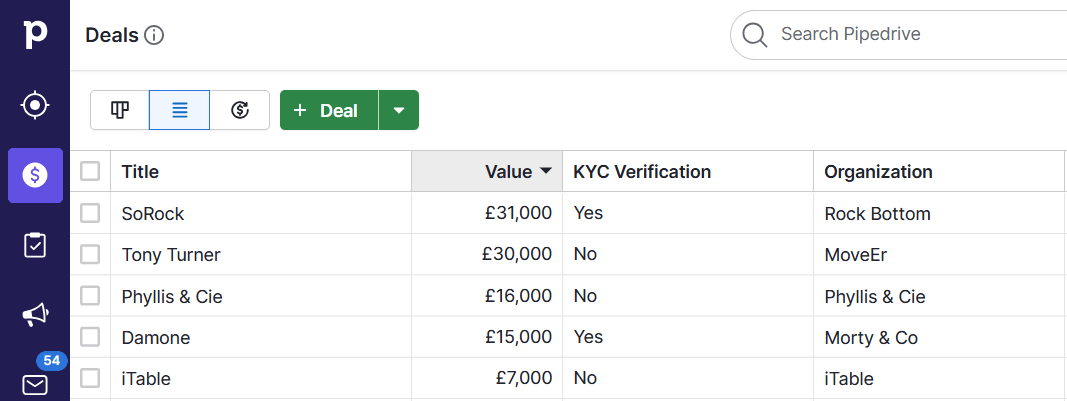
To use this feature, simply create a custom field for “Compliance” and mark it as complete when the relevant checks are complete.
7. Be transparent about AI use
Companies are responsible for telling customers how they use AI to handle their data. Transparency is a fundamental aspect of both the EU AI Act and the NEST AIRMF.
Being transparent about AI use means publishing details about AI-driven risk management processes, ideally on a dedicated page on your company website. Pipedrive’s Trust Center is a good example.
Transparency also means providing accessible explanations of AI risk assessment methodologies and AI-generated decisions.
What’s the role of AI governance in AI risk management?
AI software providers and organizations that use their tools are responsible for ensuring that AI is not harmful.
AI governance formalizes these responsibilities by setting rules for AI use and development.
There are two major pieces of governance to know: the AI Risk Management Framework and the EU AI Act.
The AI Risk Management Framework
The US offers the AI Risk Management Framework (AIRMF) from the federal government agency NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology).
The NIST AI Framework is an example of “soft governance” because it’s voluntary, and there are no penalties for failing to comply. It provides helpful guidance for organizations by:
Establishing norms and expectations for responsible AI use, including transparency, fairness and accountability
Providing a structured approach for managing risk through four key functions: “Govern”, “Map”, “Measure” and “Manage”
Setting industry standards for best practice by offering guidelines and actions for addressing AI challenges like security and bias
The EU AI Act
The EU Artificial Intelligence Act (also known as the EU AI Act) is a regulatory and legal framework for AI development and use in the European Union. It’s the most comprehensive and stringent piece of AI legislation in the world.
The EU Act applies to both AI systems providers and organizations using AI in a professional context.
It applies to any AI product available on the EU market, meaning US-based software providers with tools available in Europe must follow the rules.
The EU is rolling out the act’s provisions in a phased program of initiatives. Implementation dates fall between six and 36 months after 1st August 2024, when the EU AI Act was enacted.
The legislation sets out a risk-based framework, as shown below. It sets out rules for different types of AI based on the level of risk they present to “an individual’s health, safety or fundamental rights”.
The levels of risk under the EU AI Act are:
Unacceptable risk. Prohibited systems that pose a severe threat to safety or human rights (e.g., social scoring)
High risk. Systems used in critical sectors that require strict compliance (e.g., healthcare diagnostics)
Limited risk. Systems with moderate risk that require transparency obligations (e.g., chatbots)
Minimal risk. Systems with negligible risk that require minimal legislation (e.g., spam filters)

Under the Act, AI systems that pose an “unacceptable” level of risk are banned outright.
These risky systems include some social scoring tools that make predictions about users based on their socioeconomic backgrounds. For example, some customer loyalty programs might use AI to identify and exclude customers based on personal characteristics.
Unlike the NIST framework, the EU AI Act is an example of “hard governance”. It’s not voluntary, and there are hefty financial penalties for failing to comply.
The most significant breach is continuing to use a prohibited system. It results in a fine of up to $36.6 million or 7% of a company’s global annual turnover, whichever amount is higher.
What does the future hold for AI and risk management?
Provisions from the EU AI Act will come into force between February 2025 and August 2027.
Applications with an unacceptable level of risk will be banned. High-risk applications must comply with a stricter set of rules.
Technology providers and businesses will operate in a more regulated climate. Both will have more stringent guidelines to follow.
AI governance may become even stronger in the future. At the United Nations’ World Economic Forum in 2024, António Guterres, the Secretary General of the UN, said:
As the rules for AI development and use become stricter, the technology is likely to continue evolving at a rapid pace. The tools for risk management may become more sophisticated.
For example:
The technology might evolve to alert businesses to financial risk even faster. It could conduct real-time simulations based on macroeconomic trends and company data.
AI applications may start to learn from cybersecurity attack patterns in real time to offer greater protection.
Those responsible for risk management must stay at the forefront of developments to benefit from the technology and ensure continued compliance.
Final thoughts
AI can help organizations manage risk more efficiently and detect threats earlier. The technology can benefit a vast range of business functions and processes.
However, there are some pitfalls to navigate when using AI to support risk management. Following best practices and staying up to date with AI governance is essential.
If you’re looking for a CRM with functionality for tracking risk management activities, consider Pipedrive. Sign up for a free 14-day trial.








